
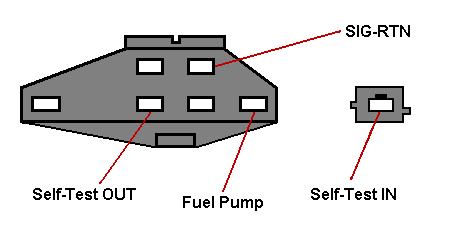
These are the main check engine light codes for MECS-II 626's. X = F/P = fuel pump relay coil (ground to activate fuel pump) W = TFA = diagnostic-mode input (? not documented for North American vehicles) U = IG- = igniter coil output (for connection to external tachometer)
1991 FORD DIAGNOSTIC PLUG JUMPING CODE
T = FAB = trouble code output (air-bag diagnostic monitor computer) R = TSC = diagnostic-mode input (cruise (speed) control computer) Q = TWS = diagnostic-mode input (? not documented for North American vehicles) P = TAC = diagnostic-mode input (? not documented for North American vehicles) N = TBS = diagnostic-mode input (anti-lock brakes (ABS) control computer) M = TAT = diagnostic-mode input (automatic transmission control computer) K = FSC = trouble code output (cruise (speed) control computer) J = FWS = trouble code output (? not documented for North American vehicles) H = FAC = trouble code output (? not documented for North American vehicles) G = FBS = trouble code output (anti-lock brakes (ABS) control computer) To learn about the steps after getting your car into diagnostic mode for MECSII equipped vehicles please read Snailman's guide.Ī = FEN = trouble code output (engine control computer)ī = MEN = switch monitor output (engine control computer)Ĭ = TEN = diagnostic-mode input (engine control computer)į = FAT = trouble code output (automatic transmission control computer) However if that does not work (as might be the case on European versions) then try to jumper pin C (TEN) to the negative battery terminal. To enter the car into diagnostic mode for MCU or MECS-II you must jumper pins C (TEN) and E (GND). EEC-IV cars have the added advantage of using EEC-IV code scanners such as the Equus 3143 or 3145. If you do not have a check engine light you will need to hook up a test lamp in order to see your CEL/MIL codes. Both EEC-IV and MECS-II can be checked using your engine's CEL/MIL light with exception to some 1993 versions that might not have a check engine light. It is comparable to morse code coming from the check engine light while the car is in diagnostic mode.
1991 FORD DIAGNOSTIC PLUG JUMPING SERIES
Mazda used MECS-II and Ford's EEC-IV system.Įrror codes are deciphered through a series of blinking check engine light (CEL) also known as a malfunction indicator lamp (MIL). Each manufacturer had their own OBD-I system.

Just because your car is OBD-I doesn't mean you'll use the same diagnostic system as an OBD-I BMW, Toyota, or Honda. which is why we have to specify the difference in methods. MECS-II is considered OBD-I, EEC-IV is also considered OBD-I. OBD-I is a blanket term and not an industry standard set of codes like we see with OBD-II.
OBD-I is a generic term given to any diagnostic system prior to 1996's introduction of OBD-II. Short history of OBD-I diagnostic systems: You will need to figure out if you have either MECS-II or EEC-IV to get the most out of this article. This article covers both MECS-II (OBD-I) & EEC-IV diagnostics for 1993-1995 Mazda 626, Mazda MX-6, Ford Probe, and other vehicles. OBD-II (1996-2002) All Models (Nothing in this topic applies to you, get an OBD-II code scanner) Diagnostic Systems for the 1993-1995 Mazda 626


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
